If you experience severe hearing loss and hearing aids can no longer provide the needed auditory support, getting cochlear implants might be your next option. “What is a cochlear implant?” one might ask. Well, a cochlear implant is a small electronic device implanted at the cochlea (part of the inner ear). It is surgically placed to bypass the damaged parts of the ear to directly stimulate the auditory nerves with electronic impulses. It helps those who are hard of hearing make sense of the noise and hear sounds.
However, these permanent hearing implants can easily cost $30,000 to $50,000. Additionally, including rehabilitation therapy, cost of external pieces, ongoing costs, and other associated costs, the total cochlear implant cost can range from $60,000 to as high as $110,000 or more in some states.
But the good news is that there are insurance options that can help cover these costs considerably, as well as financing options that can effectively help manage the expenses without insurance or the out-of-pocket costs after insurance.
This blog lays out everything from the cochlear implant procedure to overall costs, insurance, and financing options to help you plan accordingly.
How It Works
Let’s break it down step-by-step:
| Parts of Cochlear Implant | What They Do |
|---|---|
| Microphone | Picks up sound waves from the environment and converts them into a signal. |
| Speech Processor | Selects and organizes the sounds into a signal your brain can understand. |
| Transmitter & Receiver | The signal is sent as electrical impulses to the implant inside your ear through the transmitter and receiver. |
| Electrode Array | The implant's electrode array passes these impulses to the nerves that control hearing, i.e., the auditory nerve inside the cochlea. |
| Auditory Nerve | The hearing nerves send the signals to your brain, which interprets them as sound. |
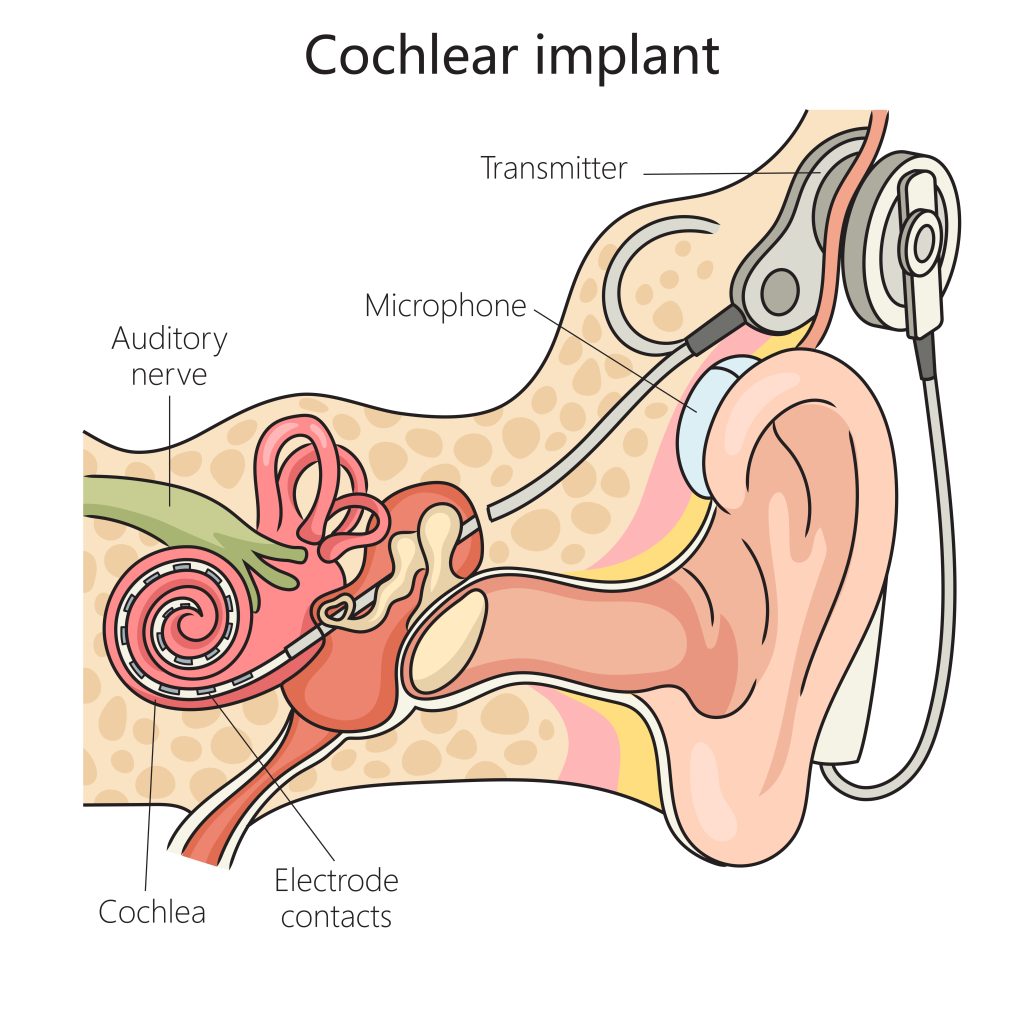
Process of Getting Cochlear Implant and the Cost at Each Phase
It’s a surgical outpatient procedure performed while putting the patient under general anesthesia.
| Phases | Description | Average Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Consultation | During the first consultation, the ENT or audiologist discusses hearing loss, medical history, and potential candidacy for a cochlear implant. | $150–$300 |
| Determining Candidacy | The patient undergoes a comprehensive hearing assessment, which includes a range of tests. | $140–$280 |
| Hearing Test | Assesses nerve function to determine candidacy through a series of tests such as audiometry, otoacoustic emissions, acoustic reflexes, etc. | $295–$650+ |
| CT Scan and MRI | Medical evaluation through imaging tests (MRI/CT scans) to assess inner ear structure. | $2,000–$3,000 |
| Cochlear Implant (CI) Evaluation | Following the CT scan and hearing tests, the evaluation is completed by the audiologist or ENT, and a treatment plan is finalized. | $270–$540 |
| Pre-Op Examinations | Involves a series of medical tests, audiological tests, and examinations like psychological and speech evaluations to assess the patient's needs for the surgery. | $300–800 |
| Cochlear Implant Surgery | It’s an outpatient procedure performed under general anesthesia. A small incision is made behind the ear to place the implant. The procedure takes 2-3 hours, and patients are discharged the same day or within 24 hours. | $30,000–$60,000+ |
| Post-op Healing | Pain and dizziness are common but subside with time. The incision heals within 2-4 weeks before the external processor is attached and activated. | - |
| Reprogramming and Activation | The external sound processor is fitted, and the initial programming and fine-tuning is done. Follow-up sessions: Usually 6 follow-up visits are required for regular reprogramming in the first year. | $1,290–$2,580 ($215–$430 per visit) |
| Rehabilitation Therapy | Intensive rehabilitation is required to train the brain to interpret new sound signals. This includes: - Auditory training to recognize speech and environmental sounds - Speech therapy for improved communication skills - Counseling for adaptation & support Sessions Needed: 20+ sessions within the first year. | $2,000–$4,000 ($100–$200 per session) |
| Annual Reprogramming | After the first year, patients usually need annual, regular check-ups to fine-tune the implant, and hearing progress is monitored. | $215 |
| Battery Replacement | Implants may require battery replacement every 2 years. | $500 |
| External Sound Processor | Typically requires replacement every 5 years or as needed based on wear and tear or technological upgrades. | $3,830–$10,700 (varies based on brand, accessories, etc.) |
| Extended Warranty (if needed) | Optional if you want extended coverage for the external processor. | Varies |
| Other Out-of-Pocket Expenses (not covered by insurance) | Includes costs not covered by insurance, such as additional therapy or accessories. | $2,000–$6,000 |
| Total Cost | $60,000–$100,000 |
How Many Post-Op Follow-up Visits Are Required?
Patients are usually required to go for follow-up visits for cochlear implant activation and reprogramming regularly.
| No. of Follow-ups | Purpose | Schedule |
|---|---|---|
| Follow-up visit 1: | Activation & Programming | Within 2 weeks to 1 month post-op |
| Follow-up visit 2: | Reprogramming | 1-month post-op |
| Follow-up visit 3: | Reprogramming | 2-month post-op |
| Follow-up visit 4: | Reprogramming | 3-month post-op |
| Follow-up visit 5: | Reprogramming | 6-month post-op |
| Follow-up visit 6: | Reprogramming | 12-month post-op |
| Annual follow-ups | Reprogramming | As needed |
| Follow up-visit 7: | For Battery Replacement | 2-year post-op |
| Follow-up visit 8: | For Sound Processor Replacement | Typically 5-year post-op (or as needed) |
How Much Does a Cochlear Implant Surgery Cost?
Almost 90% of insurance providers usually provide coverage for cochlear implant surgery. While the cost of surgery is $30,000–$55,000, the other expenses from ongoing rehabilitation, follow-up visits, and other expenses can drive up the overall cost to over $110k, but most of it can be covered by insurance.

Get personalized financing options for your cochlear implant today!
Write to UsHow Much Does a Cochlear Implant Cost with Insurance?
Patients with 100% coverage can get through without spending a dime. However, where the insurance covers 80–90% of the costs, patients may need to pay the following:
- 10%–20% as deductibles
- Co-insurance
- Co-pay
- Out-of-pocket costs
This usually amounts to around 10% to 20% of the overall cost, estimated at $2800–$6,000.
Insurance Coverage for Cochlear Implant
| Type of Insurance Plan | Maximum Coverage |
|---|---|
| Private Insurance | 80% – 90% maximum coverage (Varies based on plan) |
| Medicare | Upto 80% |
| Medicaid | 80% |
| State Programs | Partial or full coverage (varies) |
How Much Does a Cochlear Implant Cost Without Insurance?
The cochlear implant price list can range from $30,000 to over $100,000+. It varies as per the location and various other factors.
Cost of Cochlear Implants Based on Location
| State | Average Cost |
|---|---|
| California | $48,000–$100,000 |
| Arizona | $43,700–$100,000 |
| Nevada | $42,500–$116,900 |
| Oregon | $50,000–$100,000 |
| Washington | $40,800–$100,000 |
| Utah | $43,000–$100,000 |
| Idaho | $44,900–$76,900 |
| Montana | $40,400–$91,700 |
| Wyoming | $35,800–$100,000 |
| Colorado | $55,000–$93,400 |
| New Mexico | $42,880–$93,000 |
| Texas | $44,000–$104,400 |
| Oklahoma | $41,800–$120,800 |
| Kansas | $40,000–$110,400 |
| Nebraska | $43,500–$120,000 |
| North Dakota | $45,000–$100,000 |
| South Dakota | $52,500–$89,000 |
| Minnesota | $49,100–$100,000 |
| Iowa | $41,000–$114,000 |
| Missouri | $40,500–$112,000 |
| Arkansas | $41,800–$70,800 |
| Louisiana | $43,000–$94,900 |
| Mississippi | $46,900–$79,500 |
| Wisconsin | $46,700–$85,900 |
| Illinois | $42,300–$108,400 |
| Kentucky | $60,000–$100,000 |
| Tennesse | $49,000–$83,200 |
| Indiana | $53,000–$90,000 |
| Michigan | $50,000–$100,000 |
| Alabama | $38,600–$115,200 |
| Georgia | $52,000–$109,200 |
| Florida | $41,300–$113,600 |
| North Carolina | $38,315–$100,000 |
| South Carolina | $40,800–$100,000 |
| West Virginia | $41,300–$89,200 |
| Pennsylvania | $43,600–$120,000 |
| Virginia | $45,000–$100,000 |
| Ohio | $44,000–$100,000 |
| Maryland | $43,500–$120,000 |
| New Jersey | $40,000–$100,000 |
| New York | $38,900–$100,000 |
| Delaware | $30,000–$100,000 |
| Connecticut | $49,616–$100,000 |
| Rhode Island | $47,835–$100,000 |
| Massachusetts | $40,000–$100,000 |
| Vermont | $24,000–$92,010 |
| Maine | $41,900–$85,000+ |
| New Hampshire | $41,900–$100,000 |
| Alaska | $52,300–$104,900 |
| Hawaii | $30,000–$70,000+ |
Financing for Cochlear Implants
For those not covered by insurance, there are multiple options available to help manage the cost.
1. Credee Payment Plans
If paying upfront isn’t feasible, you can explore financing solutions such as Credee’s “no credit check” payment plans. This allows patients to spread the cost over manageable monthly payments that fit their budget. It helps make cochlear implants more affordable and accessible.
2. Medical Loans
Many providers offer loans or credit options for medical procedures like cochlear implants. To qualify for these, you may need a credit score of 620 or above for favorable terms. However, interest may be higher for those with a low credit score. It’s crucial to carefully understand the repayment terms to make informed financial decisions.
3. State Programs & Grants
There are also state programs, non-profit organizations, and grants in every state that may assist individuals with the cost of cochlear implants. Programs such as the Cochlear Implant Assistance Program or state-funded healthcare initiatives may help cover full or partial costs.
So, when insurance isn’t viable, it’s best to consult with your healthcare provider and explore the best financing options that fit your financial situation.
Cochlear Implant Vs Hearing Aid
| Criteria | Hearing Aids | Cochlear Implants |
|---|---|---|
| Why It's Needed | Supports weakened sensory cells in the inner ear to receive and send the sounds to the nerve. | Can be recommended when the sensory cells are too damaged and hearing aids are no longer effective. |
| Mechanism | Amplifies sound to enhance hearing. | Implanted in the cochlea to directly stimulate the auditory nerves. |
| Ideal for | Individuals with mild to moderate hearing loss who can still process amplified sounds. | Individuals with severe hearing loss who experience limited benefit from hearing aids. |
| Surgical Requirement | Non-invasive and can be easily worn or removed from the ear. | Requires a surgical procedure for permanent implantation. |
| Average Cost | $1,500–$7,000+ | $30,000–$50,000 |
What to Expect After Cochlear Implant Surgery?
| What to Expect After Surgery | - You may have a bandage on your head to protect your ear. - Mild to moderate pain around the ear is common for 1-2 weeks. Over-the-counter painkillers can help. |
| What Precautions to Take | - Do not wash your hair for at least 7 days. - Avoid straining, heavy lifting, or blowing your nose too hard for 2 weeks. - You may feel dizzy or off-balance for a few days, so avoid driving. - Take 1-2 weeks off work to allow proper recovery. |
| What to Expect During Recovery | - You might experience ringing or roaring (tinnitus), which usually improves as your ear heals. - Some people notice popping, crackling, or pulsing sensations—this is normal and will settle over time. - Bruising behind the ear and down the neck may occur, which usually goes down within 2-3 weeks. - Dizziness or nausea may occur due to the inner ear disturbance. It may take a few days to subside |
| When to Seek Help | Contact your doctor if: - You have increasing pain that isn’t relieved by painkillers. - The wound or skin above the processor becomes red, swollen, or starts oozing discharge. |
| Potential Risks | The possible complications may include: - Increased risk of meningitis or other infections - Nerve damage and facial paralysis - Dry mouth or taste changes - Balance issues or vertigo - Risk of defects or implant failure - Risk of complications from surgery like spinal fluid leak |
Bottom Line
When hearing aids are no longer an option, a cochlear implant may be the ideal solution for some. However, the cost can be exorbitant without insurance, so if you are not covered under insurance, you may want to explore your financing options. For instance, no credit check payment plans can be a great alternative to paying in easy monthly payments. Additionally, you may explore any state grants in your area that you might qualify for.
If you want to explore how Credee’s flexible payment plans may help you pay for cochlear implants, you can contact our team to learn more.
Cochlear Implants FAQs: More Insights Here
1. What Is a Cochlear Implant?
It is an advanced hearing device with part of the implant inside the inner ear structure working in connection to an external speech processor. The external device catches the sound waves and converts them into understandable electrical impulses to stimulate the auditory nerves, allowing the brain to interpret sound.
2. What Is the Cost of a Cochlear Implant?
Without insurance, a cochlear implant’s price ranges from $30,000–$50,000 to over $60,000–$110,000 overall, including ongoing rehabilitation, upgrades, parts, accessories, and other costs.
3. What is an Invisible Cochlear Implant?
Unlike traditional cochlear implants, where patients need to wear an external device on their ear, the invisible cochlear implant is implanted in the inner ear and skull, hence, concealing the implant. However, these are still in the testing stage and are only available through clinical trials.
4. How Much Does a Cochlear Implant Cost with Insurance?
With a plan that offers 100% coverage, patients don’t need to incur any cost other than any external expenses. However, with a plan that covers 80%–90% of costs, it’s generally around $2,000–$6,000.
5. Can Cochlear Implants Restore 100% Hearing?
No. They cannot restore hearing back to perfectly normal, but they can help directly stimulate the nerves that help you understand noise more clearly.
6. Who Is an Ideal Candidate for Cochlear Implants?
If a person’s hearing threshold is at or above 80 dB at multiple frequencies and they cannot hear properly despite hearing aids, it is considered to be severe hearing loss. It generally indicates a need for better hearing support, which cochlear implants may be able to provide.
7. How Much Does It Cost to Replace a Speech Processor for Cochlear Implants?
With insurance, it can cost around $5,000. If you trade in the previous processor, the cost can be lowered to $3,850–$4,890 or $7700–$10,000+; though depending on the brand, accessories, and the latest technology, it may cost more for an upgrade.
8. Why Cochlear Implants Are Bad?
These permanent hearing implants may be harder to get used to than hearing aids. After the surgery, you may experience some possible side effects, such as dizziness, nausea, and in rare cases, infection, nerve damage, meningitis, or even the loss of residual hearing ability.
Find out how Credee can help you finance your cochlear implant without financial stress!
Talk to Our Team